Why We Built ADM: Making Data Observability Conversational

Part 1 of 2: The strategic shift to agentic AI for enterprise data management
Why We Built ADM
In 2023, we started seeing a fundamental shift in how enterprises interact with complex systems. Not through better dashboards or more intuitive UIs, but through agentic AI—intelligent systems that could understand intent, orchestrate tasks, and take action.
The pattern was clear across the industry:
- Coding Agents transformed how developers write code
- GPT's changed how people access knowledge
- Agent frameworks like LangChain and AutoGPT showed that AI could do more than just answer questions—it could execute complex workflows
We looked at ADOC, our 6-year-old data observability platform, and saw an opportunity.
ADOC had evolved into a comprehensive system: monitoring data assets across warehouses, executing quality policies, tracking pipeline health, detecting drift, managing lineage. It was powerful, but that power came with complexity. Like many enterprise platforms, users needed deep domain knowledge to navigate effectively. You had to know which subsystem held the answer, which metrics to correlate, how different views connected.
This complexity isn't a failure—it's the natural consequence of building something comprehensive. The real question was: could we add a layer that made all that sophistication accessible through conversation?
More importantly: could we go beyond just answering questions to actually automating data management workflows at scale?
That's what ADM became: a strategic bet on agentic AI as the next interface paradigm for enterprise data platforms. Not because the existing UI was broken, but because we saw where the industry was heading and wanted to be there first.
The vision was ambitious: what if a data engineer could say "implement quality monitoring for all customer tables" and have an AI agent analyze hundreds of assets, generate appropriate policies, deploy them across distributed infrastructure, and report results—all autonomously? What if investigating a data incident wasn't about navigating dashboards, but having a conversation that pulled context from multiple systems?
We didn't rebuild ADOC. We built an intelligent orchestration layer on top of it.
What is ADM?
ADM (Acceldata Data Management) is an agentic AI platform that sits on top of ADOC, transforming complex data operations into natural language conversations.
ADOC remains the robust foundation—monitoring data assets, executing quality policies, tracking pipeline health. ADM adds intelligent orchestration, letting users interact with all that power through conversation instead of navigation.
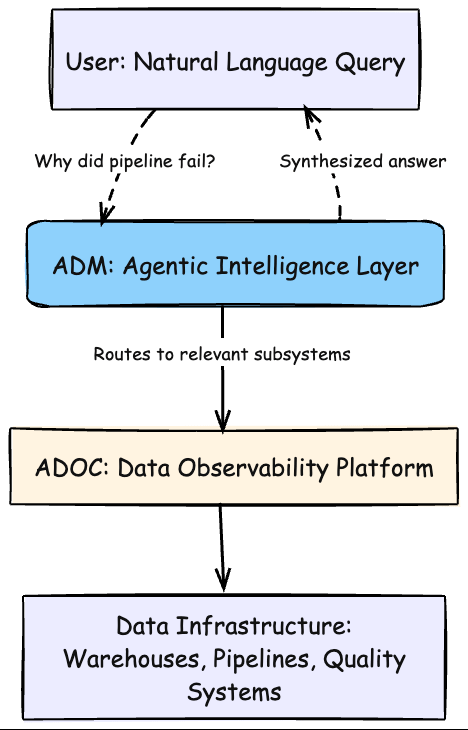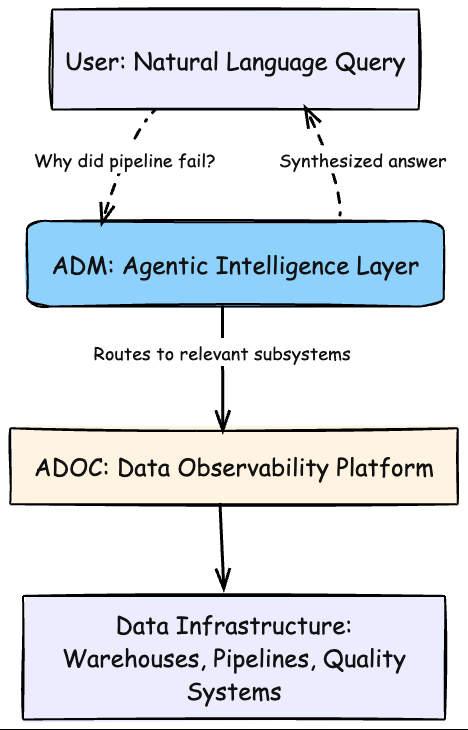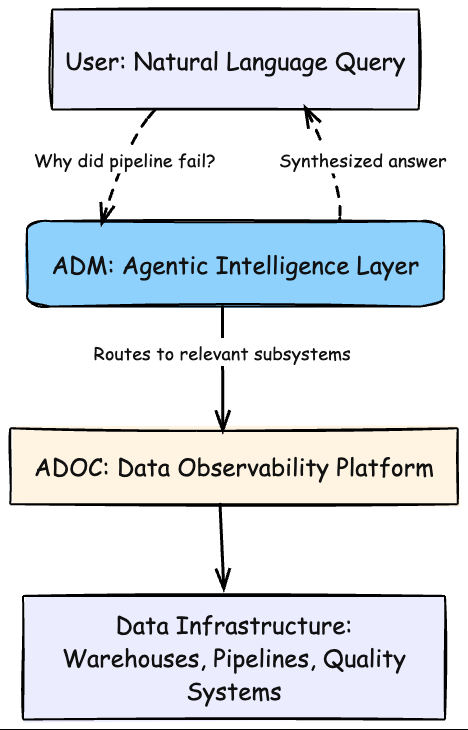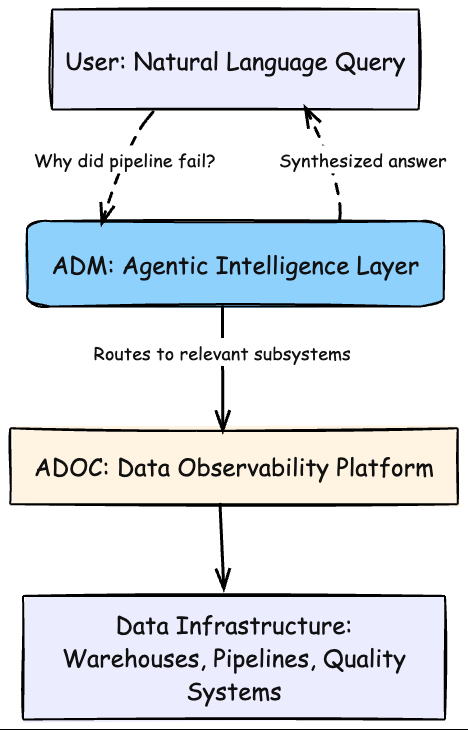
What Is It For?
The agentic architecture we built enables capabilities that go far beyond traditional data management interfaces. Here's what becomes possible when you combine intelligent orchestration with enterprise-scale execution.
1. Conversational Data Exploration
The most immediate value: eliminating the expertise barrier for data exploration.
Traditional ADOC requires knowing which subsystem to check, which metrics matter, how to construct complex queries. ADM inverts this—you express intent in natural language, and the system figures out the execution plan.
Ask: "Which customer tables have quality issues this month?"
The system:
- Routes to Catalog Agent (identify customer tables)
- Routes to Quality Agent (check policy violations, scores)
- Synthesizes results across 1,000+ assets
- Returns prioritized list with actionable context
Impact: Users now interact with 70% of ADOC features (up from 30% through the traditional UI). Business analysts who couldn't write SQL can independently investigate data quality. Data engineers spend less time answering repetitive questions.
2. Autonomous Workflow Execution
This is where agentic AI shows its real power: declarative automation at enterprise scale.
Instead of manually configuring policies, building dashboards, or scheduling jobs—you define the objective and let agents execute the entire workflow autonomously.
Example:
User: "Implement comprehensive quality monitoring for all customer tables"
ADM Agent Workflow:
1. Catalog Agent identifies 1,000+ customer-related assets across warehouses
2. Quality Agent analyzes each asset's characteristics and usage patterns
3. Workflow Agent generates appropriate policies per asset type
4. Dataplane deploys policies across distributed infrastructure
5. Execution agents run initial assessments in parallel
6. Synthesis layer reports results with recommendations
Measured impact: Manual policy configuration that previously required 2-3 weeks for 1,000 assets now completes in 4-6 hours through autonomous agent execution—a 90%+ reduction in configuration time.
The key architectural enabler: Dataplane integration. Most AI chatbots can suggest what to do. ADM can actually do it—deploying policies across thousands of assets, executing quality checks at scale, orchestrating complex multi-step workflows.
3. Cross-System Intelligence
Through MCP integration and the knowledge base, ADM creates a unified intelligence layer across your entire data ecosystem.
Knowledge Base (RAG System): Upload compliance documents, runbooks, incident reports, architectural decisions. ADM doesn't just store them—it builds a retrieval-augmented generation system that surfaces relevant context during agent execution.
Ask about a data quality metric, and ADM can pull:
- Current metric values from ADOC
- Historical context from past incident reports
- Compliance requirements from uploaded regulations
- Remediation approaches from knowledge base
MCP Connectivity: Agents can correlate data quality issues with application logs, monitoring systems, CI/CD pipelines, ticketing systems—anything connected via MCP. This turns incident investigation from a single-system query into a cross-platform correlation exercise.
4. Collaborative Intelligence
Multi-user real-time workspaces turn data exploration into a team activity with persistent context.
Multiple users can:
- Participate in the same conversation simultaneously
- @mention teammates and agents for specific expertise
- Build on previous analyses without losing context
- Create shared workbooks with reusable investigation workflows
- Document decisions in-place for future reference
The architecture benefit: every conversation becomes organizational knowledge. Past investigations are searchable. Successful analysis patterns become templates. The system gets smarter as teams use it.
This shifts data management from individual firefighting to collaborative problem-solving with institutional memory.
Real-World Use Cases
Here are two actual examples from production ADM usage:
1. Root Cause Analysis Through Visual Correlation
The Question:
"Show me a line chart of the DQ scores for the revenue_transactions policy
over the last 7 days and overlay record processing volume"
What ADM Did:
- Quality Agent pulled 7 days of policy execution data
- Pipeline Agent retrieved record processing volumes
- Generated a dual-axis line chart overlaying both metrics
- Analyzed the correlation pattern
The Insight (28 seconds):
ADM identified the root cause automatically:
- DQ scores started at 100%, dropped to 95.24% starting Sep 20
- Processing volumes spiked from ~80-244 records to 8,000-10,000 records on Sep 20
- Quality degradation directly correlated with volume spike
- Higher volumes (8K+ records) showed 52-80 failed records
- Conclusion: The policy can't handle high-volume processing
The Impact:
Traditional approach: Engineer opens quality dashboard → checks policy history → opens pipeline dashboard → exports both datasets → builds chart in Excel → manually correlates patterns (30-45 minutes)
ADM approach: Ask one question, get visual correlation analysis with root cause identified (28 seconds)
2. Asset Discovery and Policy Audit
The Question:
"What policies are attached to the processed_transactions table?"
What ADM Did:
- Catalog Agent identified the asset
- Quality Agent queried all attached policies
- Synthesized policy metadata with context
The Response (22 seconds):
Found 2 active policies:
- Data Quality Policy:
transaction_balancing_check- Type: Asset-level policy
- Focus: Revenue transaction balancing
- Created: July 24, 2024
- Schema Drift Policy:
processed_transactions_schema_monitor- Type: Auto-created from data source settings
- Focus: Structural changes to table schema
- Created: August 3, 2024
Also noted: No reconciliation, data drift, or data cadence policies attached (potential gap)
The Impact:
Traditional approach: Navigate to asset details → click through policy tabs → manually check each policy type → compile list (5-10 minutes per asset)
ADM approach: Natural language query returns complete policy inventory with contextual gaps identified (22 seconds)
This becomes powerful when auditing hundreds of assets: "Show me all financial tables missing reconciliation policies" — answered in seconds instead of hours of manual checking.
What's Next
In Part 2: "How ADM Works: An Architectural Overview", we'll dive into the technical architecture:
- Multi-agent orchestration and dynamic tool selection
- The data abstraction layer that bridges legacy systems with modern AI
- Hybrid scale-out architecture through Dataplane integration
- Hallucination prevention and enterprise security patterns
We'll explore the design decisions, trade-offs, and architectural patterns that make ADM work at enterprise scale.
This is Part 1 of our ADM series. Read Part 2: How ADM Works for the technical deep-dive.